MLOps The Series: Ep.1 — Introduction to Machine Learning System
Published:
Hi everyone, welcome to MLOps the Series.

In nowadays, machine learning is rapidly tranforming how we interact with technology and solve complex problems. But what exactly is machine learning, and how does it transition from an exciting concept to a practical, realiable solution? Let’s break it down in this blog.
What is Machine Learning?
At its core, machine learning is an approach to learn complex patterns from existing data and use those patterns to make predictions on unseen data. It’s not about explicit programming; instead, ML systems learn from the data you need to feed them. This capability makes ML suitable for:
- Repetitive tasks
- Large-scale operations
- Situations with constantly evolving patterns
However, ML isn’t a magic bullet. It shouldn’t be used when simpler solutions are available, if it’s not cost-effective, or if it raises ethical concerns.
The Machine Learning Project Life Cycle
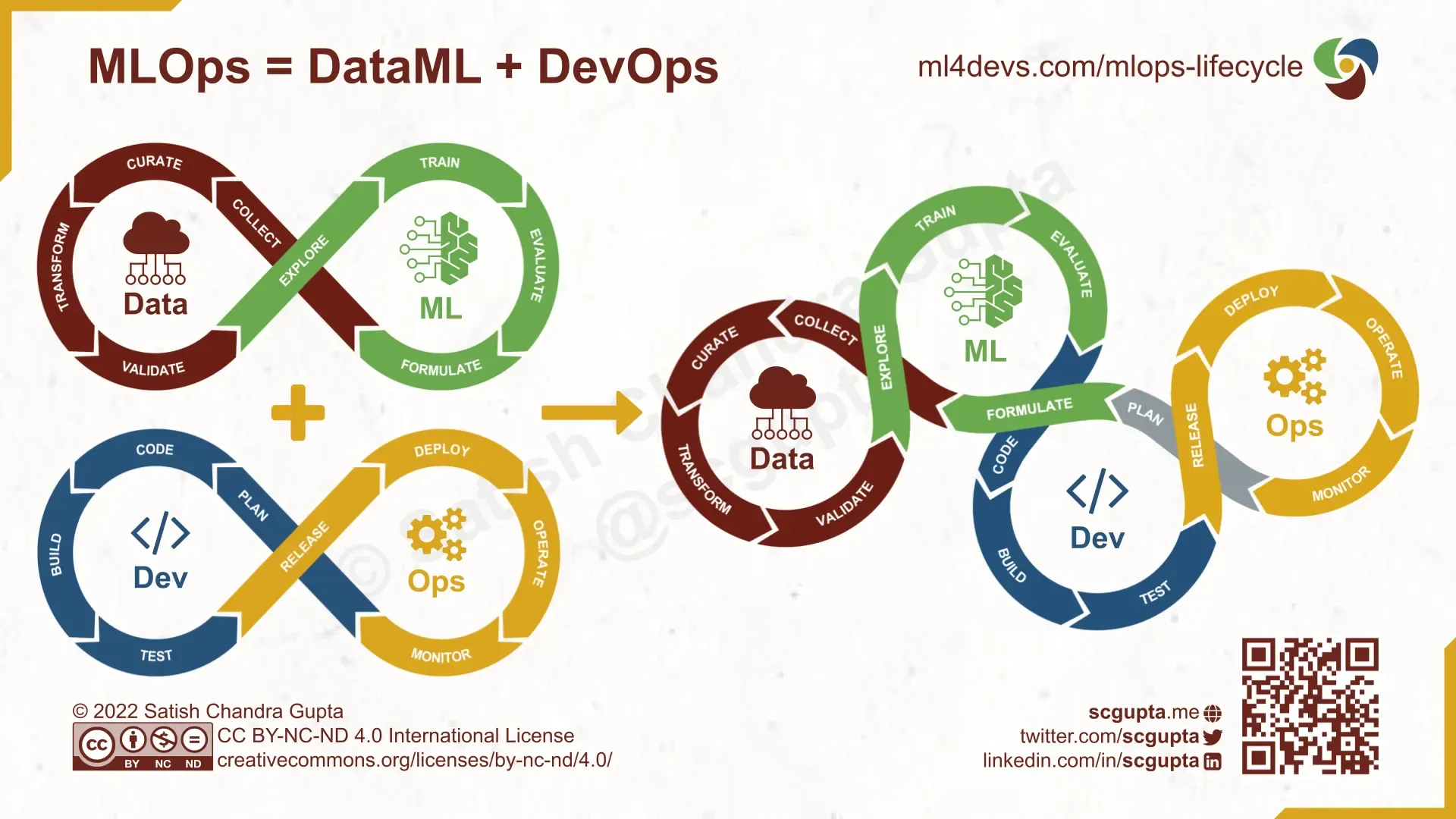
Developing a machine learning system involves a series of steps:
- Data Collection and Preparation: This includes creating data pipelines and feature engineering. Data must be accurate, reliable, and accessible. It’s crutial to understand data properties and how to combine different sources.
- Model Development: Data Scientists build models based on business needs. This involves model training, evaluation, and hyperparameter tuning. Experiment tracking tools and version control are crucial for reproducibility.
- Deployment: ML Engineers build operational systems and conduct testing for security, performance, and availability. Models can be deployed as a service via an API or embedded within an application. Containerization technologies like Docker help ensure consistent deployment environments.
- Mornitoring: This involves tracking the model’s performance, resource usage, and its impact on the business.
What is MLOps?
MLOps (Machine Learning Operation) is the parctice of streamlining the ML lifecycle. It’s more than just a technical process; it’s a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement, which aims to
- Speed up development: Help data scientists and engineers work together more effectively.
- Improve reliability: Ensure models work well, even under pressure.
- Manage risks: Reduce the chances of model failure, inaccurate preductions, and loss of skills.
- Maintain Quality: Keep track of model versions (like version control) and ensure that model performance is not degrading in production.
Who’s who in the ML Team?
For the very successful result in the certain machine learning project, the team might need to diverse roles as follow:
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Provide business goals and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
- Data Scientists/ML Researchers: Build and evaluate models
- Data Engineers: Set up data pipelines
- ML Engineers: Build and maintain operational systems; they are software engineers with ML skills.
- ML Product Managers: Understand the ML development process.
The Nitty-Gitty: MLOps in Action
MLOps involves several critical steps:
- Business Objectives: Defining what the model is supposed to achieve. This ususally includes performance targets, technical requirements, and cost constraints.
- Data: Finding, evaluating, and preparing data. This involves addressing questions arpund data accuracy, reliability, accessibility, and real-time availability.
- Feature Engineering: Turning raw data into meaningful inputs for the model.
- Model Training and Evaluation: Experimenting with algorithms and tracking results. This involves ensuring reproducibility by tracking environment data and using version control.
- Production and Deployment: Moving the model into a usable environment. This can be done through a model-as-a-service REST API or embedding it in an application. Containerization technologies like Docker can help with this
- Monitoring: Tracking performance from different perspectives including speed, memory and processing time, model degradation over time, and business value.
- Feedback Loop: Comparing model performance in live settings through A/B testing or shadow testing.
MLOps is about Governance
Governance is essential for ethical and responsible ML. This involves:
- Data Governance: Making sure the data is used appropriately and ethically, respecting privacy. This also involves being aware of bias and ensuring it is addressed.
- Process Governance: Ensuring governance considerations are addressed at the right points in the ML lifecycle.
The Human Side of ML
- Don’t forget the user experience:
- Consistency: The system should provide the same results under the same conditions.
- Human-in-the loop: User feedback is essential.
- Smooth Failing: Having backup options for the time that the main model is not working properly.
Resposible AI
- ML needs to be developed responsibly with consideration for:
- Fairness: Addressing potential biases in data, labeling, features, model objectives, and evaluations.
- Transparency: Understanding the limitations of data-driven models/
- Accountability: Being responsible for how the model affects user.
Key Takeaways
Machine Learning is just not only about algorithms. It’s about a holistic process that involves a diverse team, careful planning, and a constant feedback loop. MLOps is a culture that enable faster, more reliable, and ethical ML deployment. By considering these aspects, we can move ML beyond research and into real-world applications that bring value to all stakeholders.